Intel, the renowned chipmaker, is undergoing a significant transformation in its CPU branding to enhance clarity and simplify its product lineup. With the impending release of the highly anticipated Meteor Lake processors, Intel is streamlining its naming architecture, eliminating redundancies, and introducing the Intel Core Ultra processors for its highest-tier chips.
Why This Change?
Intel faced a challenge in maintaining a diverse range of processors for various power limits, speeds, costs, and target audiences while keeping the naming scheme minimal and easily comprehensible. The previous naming scheme, including Performance-cores, Efficiency-cores, U-, P-, and H-series mobile processors, and Intel Evo, contributed to the complexity. In contrast, competitors like Apple achieved simplicity with their ‘Axx’ and ‘Mx’ processors, where the ‘x’ represents the generation number. It’s very simple to understand for mass consumers. Intel recognized this and the need to streamline its branding, making it more consumer-friendly.
“Our client roadmap demonstrates how Intel is prioritizing innovation and technology leadership with products like Meteor Lake, focused on power efficiency and AI at scale. To better align with our product strategies, we are introducing a branding structure that will help PC buyers better differentiate the best of our latest technology and our mainstream offerings.”
–Caitlin Anderson, Intel vice president and general manager of Client Computing Group Sales
All The New Changes
To address the confusion surrounding its CPU branding, Intel has made the following changes:
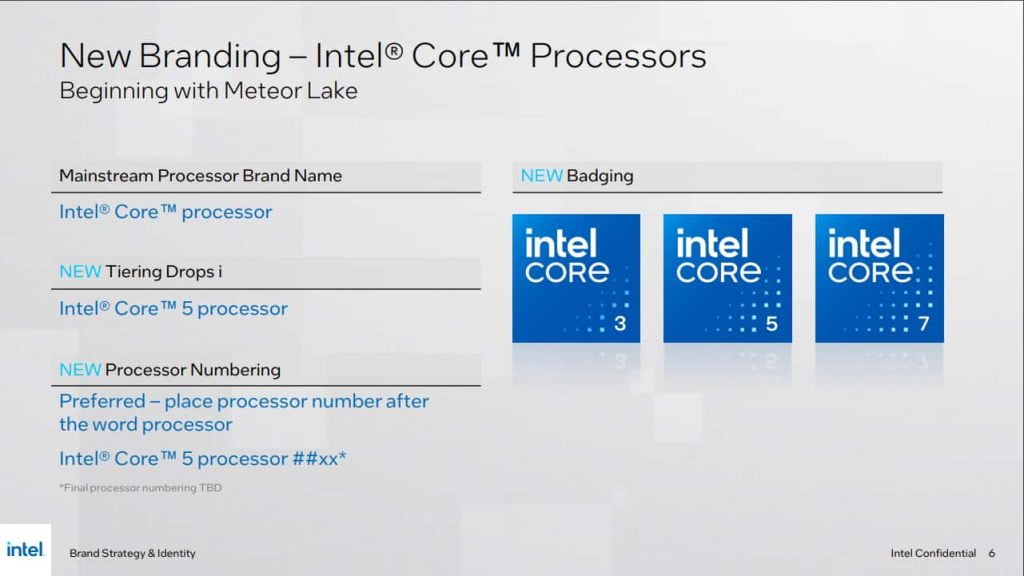
- Removal of the ‘i’ from Intel Core branding: The famous ‘i’ is dropped from all Intel Core processors, resulting in simplified names such as Intel Core 7-1355U.
- Elimination of the ‘Intel 14th Gen’ labeling: The generation number is now included in the processor number itself, e.g., Core 7-1355U, where ’13’ signifies the 13th generation designation.
- Introduction of Intel Core Ultra processors: Intel Core Ultra represents the highest-tier chips, offering enhanced performance and cutting-edge features.
- Referring to Intel Evo-certified laptops as Intel Evo Editions: Intel Evo Edition laptops are distinguished by their exceptional performance and superior user experience.

Intel’s New Naming Scheme:
Here’s a simple example of how the new naming scheme actually works:
- Mainstream Processor Brand Name: Intel Core processor.
- Processor Tier: Intel Core 5 processor.
- Processor Number: Intel Core 5 processor ##xxU/P/H, where ‘##’ represents the generation number, ‘xx’ denotes the processor number, and U/P/H signifies the power tier.
The all-new Intel Core Ultra Processors
One significant change is the introduction of the Intel Core Ultra processors, representing the highest-tier chips in Intel’s lineup. Here’s what you need to know:
- The Intel Core Ultra processors will be positioned as the flagship parts, offering top-notch performance and advanced features.
- These processors will have “bigger feature sets” and may include Arc-level graphics integrated into the processor, setting them apart from mainstream Core processors.
- The exact details of the Core Ultra processors are yet to be disclosed by Intel.
- Enthusiasts and technical users can still access detailed information about the processors through the full alphanumeric identifier.
- Intel provides examples of the new naming convention, such as:
- Intel Core Ultra 9 processor 1090H: A flagship laptop processor with powerful onboard graphics.
- Intel Core Ultra 7 processor 1070K: A powerful desktop processor unlocked for enthusiasts to overclock.

These changes aim to provide consumers with a more straightforward naming scheme and better differentiate Intel’s product offerings. With the introduction of the Intel Core Ultra processors, users can expect top-tier performance and advanced features to meet their computing needs.
Implications and Benefits of These New Changes
The revamped branding strategy by Intel provides several advantages:
- Enhanced Clarity: The simplified naming structure reduces complexity and improves understanding for consumers, retailers, and OEMs.
- Clear Product Differentiation: The introduction of Intel Core Ultra processors allows for a distinct separation between flagship parts and mainstream offerings, catering to varying user requirements.
- Alphanumeric Identifier: Enthusiasts can still access the full alphanumeric identifier to determine the capabilities and generation of a specific chip.
- Future-Proofing: The new branding approach positions Intel to adapt to future advancements and processor iterations without requiring extensive rebranding efforts.
14th Gen Meteor Lake and Windows 12 Optimizations
While Intel has not officially confirmed Meteor Lake as its 14th gen chip, it is widely anticipated. Rumors suggest that Meteor Lake processors, alongside the forthcoming Windows 12 operating system, will be optimized for each other. Intel’s Vision Processing Units (VPUs) are expected to play a crucial role in Windows 12, aligning with the OS’s AI-driven focus. Competitors such as Qualcomm and AMD are also venturing into AI, posing formidable challenges in this space.
Conclusion:
Intel’s decision to simplify its CPU branding by removing the ‘i’ and introducing the Intel Core Ultra processors signifies a step toward a clearer and more user-friendly experience. By streamlining the naming architecture, Intel aims to improve understanding among consumers, retailers, and OEMs. The upcoming release of Meteor Lake and its optimized integration with Windows 12 holds promise for enhanced performance and efficiency, positioning Intel as a significant player in the AI-driven computing landscape.
You can also read about the new changes from the official Intel Newsroom







